Agentic AI and How It’s Replacing Traditional AI Models
AI is moving beyond just responding to prompts with text or images. The next significant step is agentic AI, which empowers AI systems to comprehend their environment, establish objectives, and take deliberate actions to achieve them.
According to a recent report by Gartner, less than 1% of enterprise software applications used agentic AI techniques in 2024. According to the report, that number could rise to 33% by 2028. This means that more and more businesses are starting to see great value in agentic AI, and hopefully after reading this article, you will see why.
What Is Agentic AI and Why Should You Care?
There is currently no universally agreed-upon definition of agentic AI. Some people use the terms "agentic AI" and "AI agents" interchangeably, while others draw distinctions between them. Despite these differences, most agree on certain aspects of agentic AI.
Agentic AI refers to AI systems that can operate with a degree of independence, making decisions and taking actions to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional AI, which requires explicit prompts to generate results, agentic AI can analyze situations, develop strategies, and execute tasks in parallel.
Agentic AI applications maintain control of how they accomplish tasks by using tools and making decisions about internal processes.
Some key aspects that define agentic AI include:
- Autonomy: The ability to function without continuous human interaction.
- Goal-oriented behavior: Setting and pursuing objectives based on predefined or evolving goals.
- Adaptability: Responding to changing environments and learning from past interactions.
- Workflow optimisation: Moving between subtasks and applications efficiently to complete processes.
To better understand what agentic AI is, think of an autonomous vehicle that continuously recalculates the optimal route (for speed or economy) to its destination as conditions change.
How does Agentic AI differ from Traditional AI?
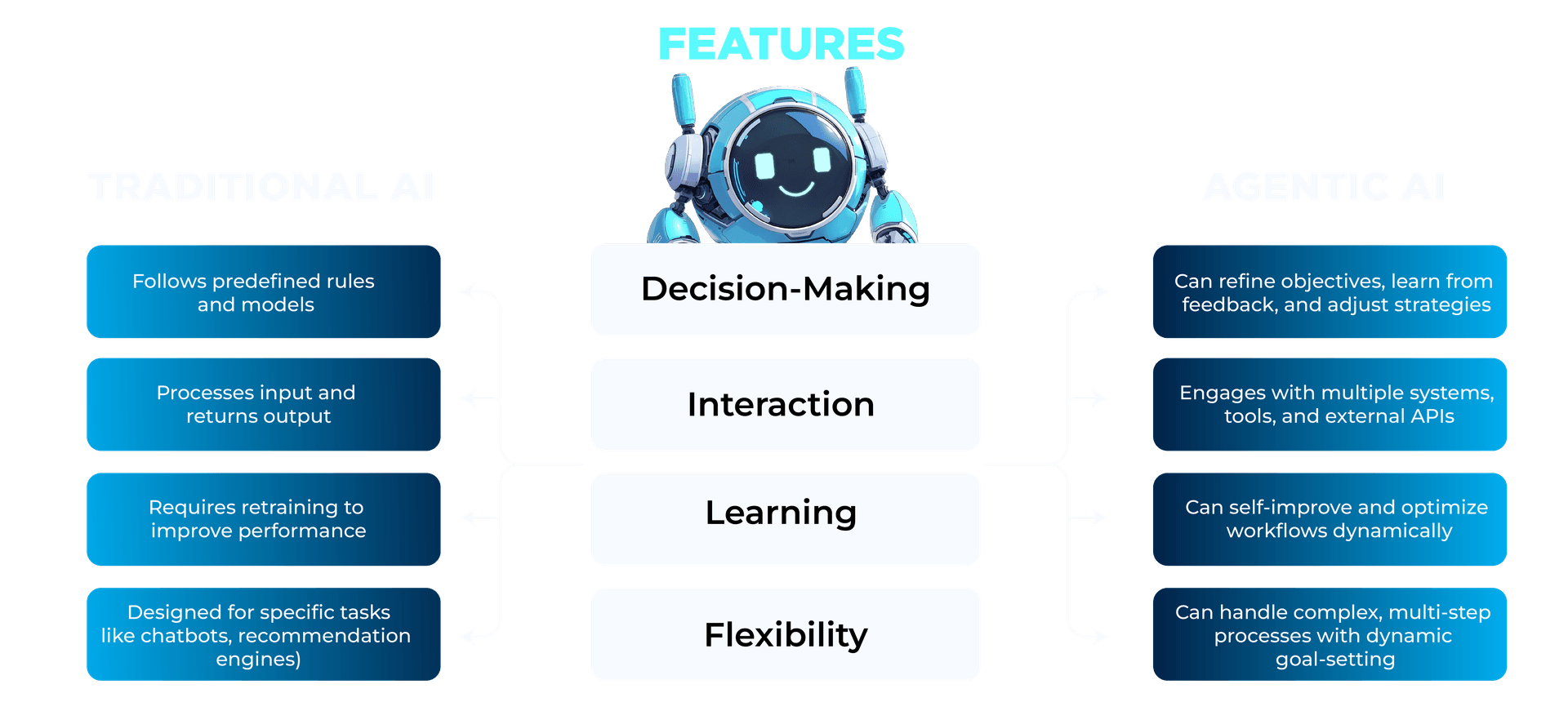
While agentic AI is a type of AI, it differs from traditional AI.
Traditional AI operates primarily on specific algorithms using largely structured data and set rules. These models are designed to perform well-defined tasks, such as sorting data, facial recognition, or language translation. The scope of traditional AI is limited to its programming and cannot deviate away from its given instructions or learn from new experiences.
On the other hand, agentic AI systems are designed to be more autonomous and adaptive. They process data and make decisions, learn from interactions, and take proactive steps toward achieving complex goals by anticipating needs and suggesting actions. The idea is to give machines agency so they act more like partners than tools.
Agentic AI leverages innovations like:
- Large language models that comprehend nuanced human speech
- Scalable computing power to train complex models
- Very large datasets to enable deep learning
- The ability to connect and interact with other systems
How Does Agentic AI Work?
Agentic AI isn’t a single technology but a way of designing AI systems that operate with more independence than traditional models. The details vary from one application to another, but most agentic AI systems involve multiple LLMs that communicate through prompts, use external tools, and can read and write files.
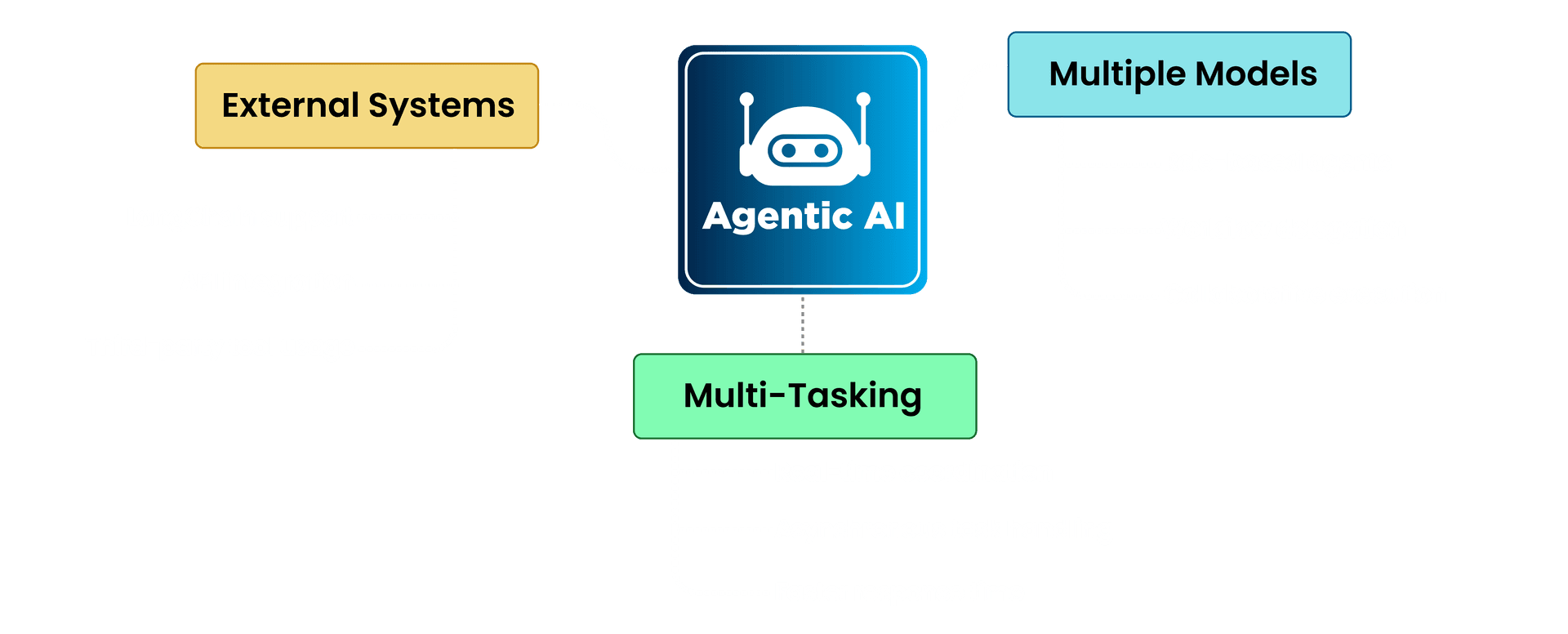
These systems often work asynchronously, making them feel more like distributed networks than isolated models.
1. Multiple models with multiple roles
In most cases, an agentic AI system isn’t just one LLM running alone, but it’s a set of models interacting with each other. A common setup involves assigning distinct roles to different models.
For example, one model might act as a task manager, breaking down complex problems and distributing subtasks to other models. These sub-models then complete their assigned work and pass their output back to the task manager for evaluation and integration.
2. External Systems
To function beyond text generation, agentic AI needs access to external tools. These could be APIs for retrieving real-world data, databases for storing information, or even file systems for reading and writing documents.
Some frameworks, like LangChain, make it easier to connect LLMs to these tools, allowing them to query databases, retrieve search results, or even interact with software applications.
3. Handles Tasks Simultaneously
Unlike traditional AI applications that process input linearly, agentic AI often operates asynchronously. Multiple models can work on different parts of a problem at the same time, which can give these systems a decentralized feel.
For example, in an AI-powered research assistant, one model might fetch relevant documents while another analyzes their contents, and yet another synthesizes a summary, all happening concurrently.
What’s Holding Agentic AI Back?
Despite its advantages, agentic AI presents significant challenges that need careful consideration. These range from ethical concerns to socio-economic disruptions and technical limitations.
Ethical concerns and regulation
One of the biggest challenges is the ethical implications of AI making autonomous decisions that affect human lives. Without clear laws and guidelines, there’s a risk of unintended harm. Until we develop robust legal frameworks and gain more real-world experience, it may be wise to limit agentic AI to assistant-based roles rather than allowing it to take direct actions with serious consequences.
The Human Cost of Smarter Machines
Agentic AI promises to handle time-consuming tasks and freeing up human workers to focus on creative, strategic, or emotionally intelligent work. That sounds great in theory. But in practice, the shift could be disruptive.
Just like with past tech revolutions, some jobs will disappear before new ones are created. The good news? History shows that while jobs change, they don’t vanish but they evolve. The key lies in preparing for that evolution. Businesses, and educators need to invest in reskilling programs and new career pathways to help the workforce transition, not just react.
AI transparency
As agentic AI systems become more advanced, tracing how they reach their conclusions becomes increasingly difficult. These systems often process vast amounts of data across multiple steps, making their logic hard to follow, even for developers.
How Will Agentic AI Impact the Businesses?
Much like generative AI before it, agentic AI is poised to streamline businesses of different shapes, sizes, and industries. According to Gartner, by 2029, AI agents will resolve 80% of common customer service issues without human intervention, leading to a 30% reduction in operational costs.
“Unlike traditional GenAI tools that simply assist users with information, agentic AI will proactively resolve service requests on behalf of customers, marking a new era in customer engagement,” said Daniel O’Sullivan, Senior Director Analyst in the Gartner Customer Service & Support Practice.
AI decision-making systems may also streamline employees’ day-to-day workflow by automating many complicated but repetitive tasks. AI trading agents, for instance, could improve how financial institutions operate by analyzing market trends and data and then automatically adjusting trading strategies for the least financial risk. McKinsey predicts that the high-quality content these agents produce could reduce review cycle times by 20 to 60%.
The Future of Agentic AI
Although the majority of today's systems automate predetermined tasks, future models are probably going to go farther like establishing their own goals and developing into more autonomous problem-solvers.
Self-improving systems
Right now, agentic AI follows human-set goals, but future versions may evolve dynamically. Instead of just executing tasks, they could refine their strategies, learn from failures, and adjust their objectives based on changing conditions. This could lead to AI systems that act more like true digital collaborators rather than just tools.
More accessible development tools
As AI development platforms improve, non-technical users will gain access to more intuitive ways of creating AI assistants. Instead of needing to code complex workflows, people will be able to design AI-powered helpers through simple interfaces. These could manage emails, automate business operations, or even handle complex project coordination without requiring deep technical knowledge.
Personalized Digital Partner
The long-term vision for agentic AI isn’t just automation but personal adaptation. AI systems will likely become more individualized, learning a user’s preferences and working style to provide customized support. Instead of a one-size-fits-all AI, each person could have a system that understands their unique needs and evolves alongside them.

Agentic AI Isn’t Just a Buzzword
Though Agentic AI shifts the narrative from “Tell me what to do” to “I’ve already done it, and here’s the result.” And that’s a game-changer. It’s not about replacing humans. It’s about augmenting your team with intelligent systems that take initiative, adapt to change, and scale effortlessly.
